GPSplit

With today’s presence of wearables and tracking Apps, there is a good chance that any outdoor activity produces data that can be downloaded as a GPX file. While there are various programs for displaying such files, a tool for performing quick modifications on such files was missing – until now.
The command-line tool GPSplit aims to solve this issue! It offers commands for splitting, merging, filtering, and simplifying GPX files.
GPSplit is available at GitHub . Its functionality will be described in the sections below.
Background#
GPX is a XML schema that defines a list of GPS coordinates (waypoints) that can be summarized in routes or track segments. The schema allows the definition of multiple routes, tracks, or individual waypoints within a single file. Additionally, a track can hold multiple track segments.
The following example visualizes the GPX format. It holds a GPX object with one track. The track contains two segments with three and two waypoints, respectively.
<?xml version='1.0' encoding='UTF-8'?>
<gpx version="1.1" xmlns="http://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1 http://www.topografix.com/GPX/1/1/gpx.xsd">
<metadata>
<name>A GPX Track</name>
<author><name>abzicht</name></author>
</metadata>
<trk>
<name>Track #1</name>
<trkseg>
<trkpt lat="49.842945" lon="9.902103">
<ele>262.454418</ele>
<time>2025-08-30T13:22:00.000Z</time>
</trkpt>
<trkpt lat="49.843061" lon="9.902099">
<ele>262.454418</ele>
<time>2025-08-30T13:22:40.000Z</time>
</trkpt>
<trkpt lat="49.844422" lon="9.902045">
<ele>260.863955</ele>
<time>2025-08-30T13:23:20.000Z</time>
</trkpt>
</trkseg>
<trkseg>
<trkpt lat="49.844340" lon="9.901424">
<ele>259.739450</ele>
<time>2025-08-30T13:24:00.000Z</time>
</trkpt>
<trkpt lat="49.844110" lon="9.899744">
<ele>257.148924</ele>
<time>2025-08-30T13:24:40.000Z</time>
</trkpt>
</trkseg>
</trk>
</gpx>
In this example, it would be straightforward to, e.g., merge the two segments into one. However, it is not untypical for GPX files to become unreasonably large. Modifying such files manually is not only tiresome, but also prone to error.
The Solution#
The idea for GPSplit was born when I found myself tackling a GPX file that spans recordings of over two years, with 134,443 waypoints that translate to 1,613,334 lines. The file defines two tracks with one track segment each(!).
The GIF below shows those two tracks – and the postprocessing after I split those into reasonable chunks using GPSplit.
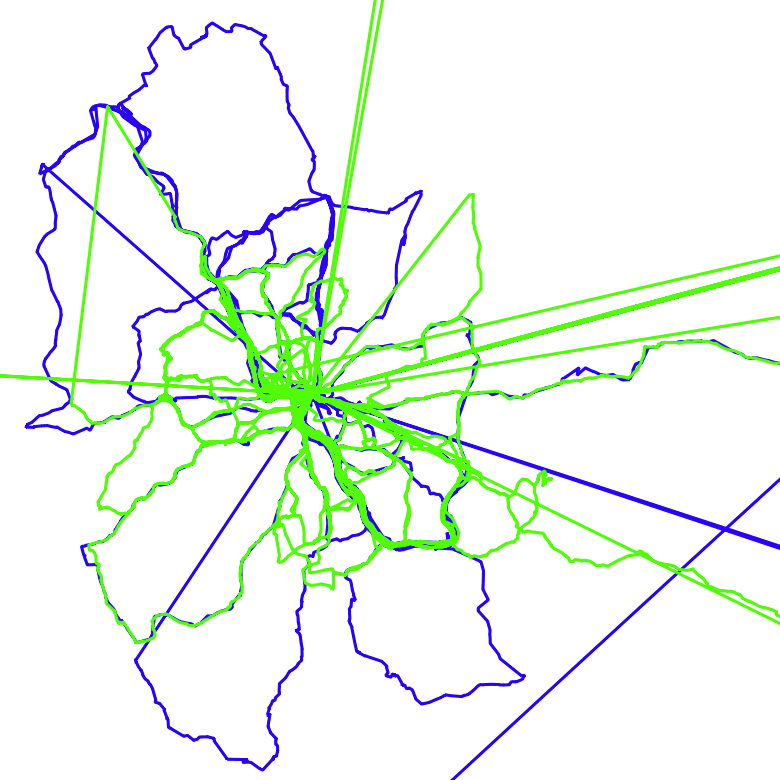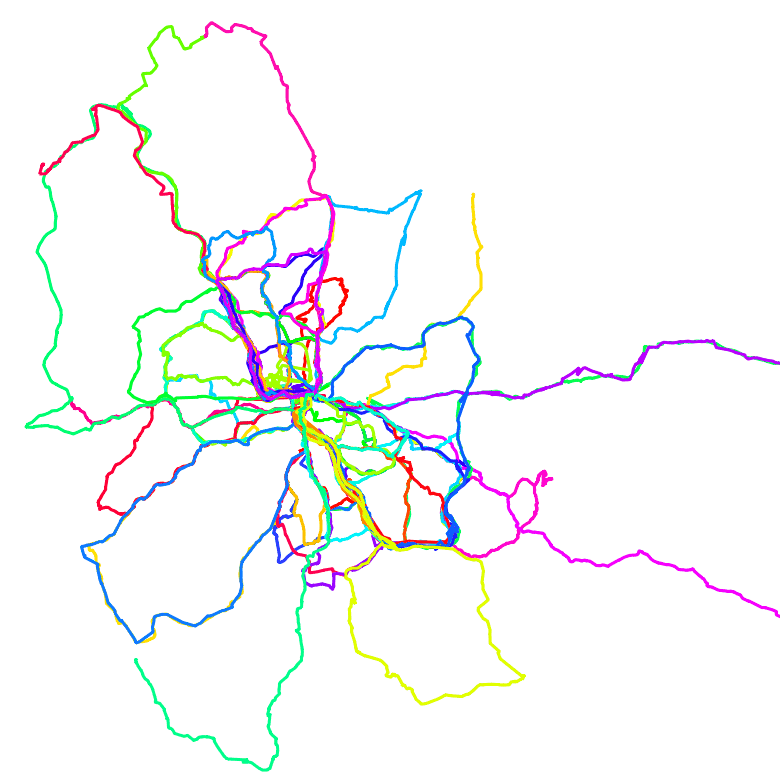
The command(s) I used for splitting the two tracks into over 100 individual ones is the following:
gpsplit -i ./my-recording.gpx split --distance 5000 --duration 8h \
--pause-split 200,1h | gpsplit filter --trim 50 | \
gpsplit -o ./gpx remove --simplify 40 \
--min-radius 1000 --min-points 80
The purpose of the utilized flags will be described in the features section below.
For now, note that GPSplit expects to be provided GPX
files via -i or via STDIN. The output of
GPSplit is written to files or folders defined via -o. If this flag is not
present, all output is written to STDOUT. This property allows multiple gpsplit
commands to be chained together, as shown above.
Features#
Besides straightforward tasks such as analyzing and merging GPX data, the more interesting features offered by GPSplit are its options for filtering and splitting files / tracks / track segments based on various conditions.
In the GIF shown above, one of the main goals for cleaning up the file was to split segments whenever a pause was detected (min. number of consecutive waypoints lie within a given radius for a given min. duration) and to trim the start and end of segments. With the following list of features offered by GPSplit, this is easily achieved.
For simplicity, GPSplit assumes waypoints to be contained within track segments. Alternative options such as routes are not (yet) supported.
Merge#
gpsplit merge \
--merge-segments \
--merge-tracks \
--merge-files
The merge command offers the unconditional merging of multiple files, tracks, and track segments.
Filter#
gpsplit filter \
--trim=100 \
--trim-start=100 \
--trim-end=100
The filter command allows waypoints to be removed at the start and/or end of a track segment. This is useful, if the start/stop of a recording does not match the begin/end of the activity that was supposed to be recorded. The command removes all waypoints that lie within a customizable distance to the first/last waypoint of the segment.
Split#
gpsplit split \
--tracks \
--segments \
--distance=10000 \
--duration=5h \
--pause-split=100,30m
This command allows tracks with multiple track segments to be split into multiple tracks with one track segment each. Likewise, files with multiple tracks can be split into multiple files with one track each.
In addition, track segments can be split, if consecutive waypoints exceed a given distance or duration. Furthermore, the pause-split option allows track segments to be split, if waypoints lie within a given radius for a given min. duration.
Remove#
gpsplit remove \
--simplify=50 \
--remove-stops \
--min-points=100 \
--min-radius=100 \
--min-distance=100 \
--min-duration=1h \
--max-duration=1d
The remove command is capable of removing entire track segments, if they
- undercut a given number of waypoints / radius / distance / duration, or
- exceed a given duration.
It also offers options for removing waypoints, in order to
- remove pauses where no significant movement takes place, or
- simplify the path, reducing the number of waypoints.
Analyze#
gpsplit analyze \
--count
The analyze command prints (statistical) information of GPX files, tracks, and track segments. By using the counts option, only the number of tracks, track segments, and waypoints is printed.
Library#
GPSplit can be used as a Go library
(github.com/abzicht/gpsplit/gpxtransform). It is, itself, built on top of
gpxgo
. It can be used to apply the
features described above directly in Go and can also be extended with, e.g.,
custom filters or splitting rules.
The github.com/abzicht/gpsplit/gpxtransform package provides functions for transforming GPX files,
tracks, and track segments. Transformations are performed based on a
config.TransformConfig object that holds transformation
functions for every desired granularity.
The following example prepares a corresponding object with a track segment transformer that splits tracks with multiple segments into multiple tracks with one segment each:
import (
"github.com/abzicht/gpsplit/gpxtransform"
"github.com/abzicht/gpsplit/gpxtransform/config"
"github.com/abzicht/gpsplit/gpxtransform/options"
)
tc := config.NewTransformConfig(config.WithTrackTransform(gpxtransform.SplitTrackBySegment()))
// corresponding functions also exist for splitting files
// based on tracks (cf. gpxtransform.SplitFileByTrack)
We can also choose to subsequently extend the tc object with segment
splitting functionality:
duration := 8 * time.Hour
distance := 5000 * unit.Metre
tc = config.WithSegmentTransform(
gpxtransform.Split(
options.TimeSplit(duration),
options.DistanceSplit(distance),
),
)(tc)
// tc now splits segments into multiple segments, if there are duration /
// distance jumps between two consecutive points that exceed the limits
Finally, we can apply the transformation on a GPX file /track / segment:
import (
"github.com/tkrajina/gpxgo/gpx"
)
reader, err := os.Open("./my-recording.gpx")
if err != nil {panic(err)}
gpxFile, err := gpx.Parse(reader)
if err != nil {panic(err)}
processedFiles, err := gpxtransform.TransformFile(*gpxFile, tc)
if err != nil {panic(err)}
// processedFiles now holds the (potentially multiple) files that we obtained
// from the transformation.
Installation#
Install Go v1.22 and run the following command:
go install github.com/abzicht/gpsplit
